CN C5 Neural Information Encoding
Information Theory and Neural Code
The rare of the symbol conveys the information.
- The lower the probability, the higher the information.
- The symbol’s Information increases as the probability of the symbol decreases.
Shannon called the average information of a code entropy.
The unit of information using base-two log is called bit.
The total information of a code is the weighted sum of the information of all its symbols.
To maximize a code’s
entropy, each symbol is used with equal probability.
e.gInformation of a code with 64 symbols:
Therefore, we need a 6-bit code to express the 64 symbols.
Neural code
There are evidence that rate-based coding have been found in many areas of brain.
e.g
- The neurons in
visual systemchangefiring ratebased on the intensity of light;- The neurons encoding small
firein proportion to the concentration of their preferred odor(气味).- The neurons in
muscleand in theskinfiremore with more pressure applied to them.
Temporal Coding
Precise timing also carries the information.
e.gSound localizationBecause of the distance between the two ears,there exists a gap between the times of arrival at each ear.
The cells in the medial superior olive (MSO) form a map where in those that signal short arrival time differences fall at one end and those that signal long differences fall at the other.
In this way, a temporal code has been transformed into a spatial code: the position of the active neuron in this map carries information about the source of the sound.
Efficiency and Redundancy
- The hypothesis: The brain performs efficient information coding.
- brain evolves to efficiently code information because of the constraints: Energy consumption. The brain consumes 20% of the body’s energy while accounting for only 2% of its weight.
- Redundancy is a waste of resources: multiple neurons say the same thing in neural systems.
Adaptation
To keep the neural code efficient, the brain needs to determine when the information is redundant.
Adaptation: The ability of the the neural system to ①track the statistics of the information it is receiving and ②match its coding scheme.
-
More specifically,
adaptationis a decline in theexcitabilitycaused by thestimulus. -
e.gIn themuscle neurons, there is a gradual decline in the neuralfiring frequencyunder a constantstimulus. -
Adaptationis a method of increasing efficiency.In information theory, if a symbol is being sent across a channel over and over, its presence no longer caries information. Thus it makes sense that the neurons stop sending spikes when they see the same stimulus repetitively.
A more specific instance, activity of the neurons that respond to motion. Visual system rapidly adapts its code to the motion information it is getting.
- To be an efficient encoder, a neuron should always
fireat its peak firing rate for the fastest motion it sees, andfireat its lowest rate for the slowest motion. - Different
firing ratesas different symbols in the neural code. Spreading thefiring ratesout this way ensures that all these symbols get used roughly equally, which maximizes theentropyof the code.
Sensory Coding Mechanisms
物理感知
大脑依赖感知神经元把外界刺激转换成脉冲信息,感知神经元起着重用的信息转换作用,类似于Analog-to-Digital,AD 转换。
Exp: 视觉信息的脉冲编码
视网膜包含2种中心环绕型神经节细胞: on-center 和 off-center。
A center-surround ganglion cell receptive field(感受野):以 off-center为例
明暗illumination敏感神经节细胞 M-type
-
a Dark spot
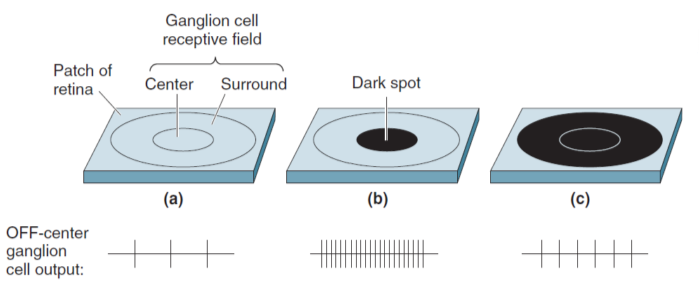
-
a light-dark edge
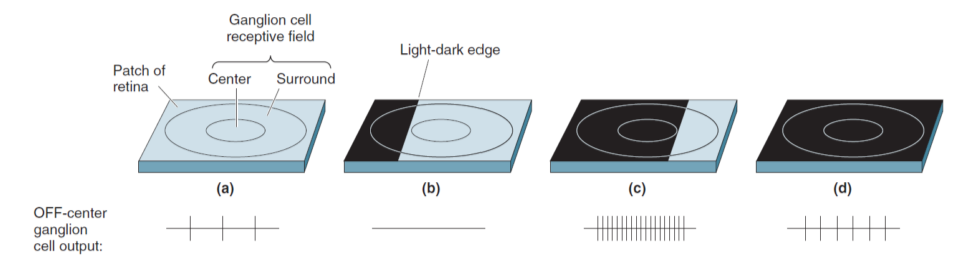
颜色敏感神经节细胞 P-type
An M-type cell from a similar retinal location is significantly larger than P-type. 主要接受视锥细胞的汇聚,负责有色视觉。实际上是对波长的反应。
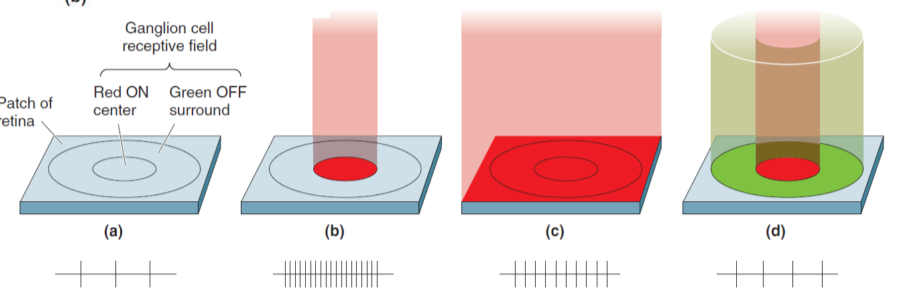
Exp: 化学感知
味觉细胞及编码
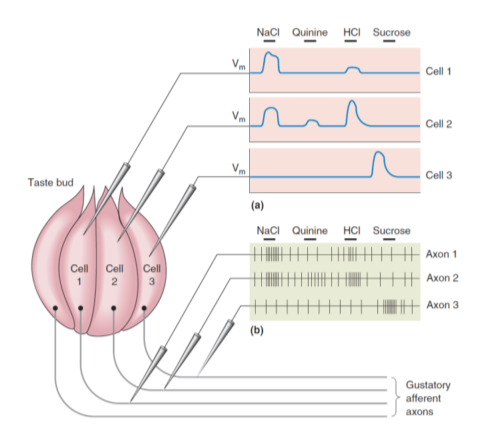
嗅觉细胞及编码
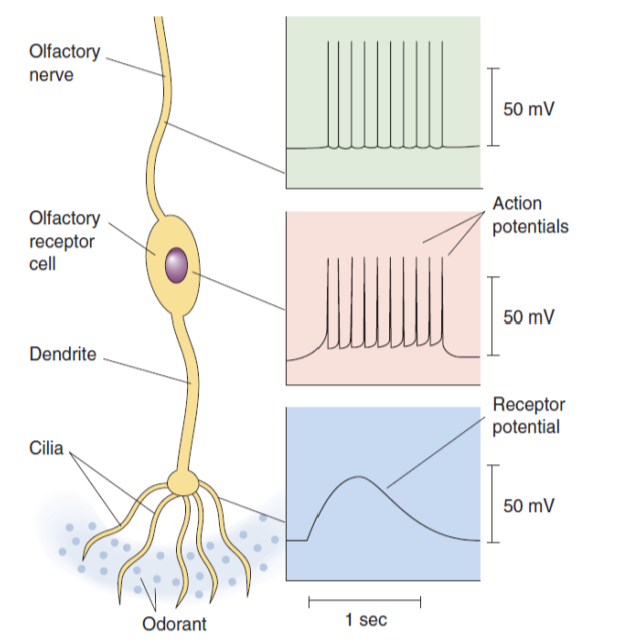
Odorantsgenerate a slowreceptor potentialin the cilia.- The
receptor potentialpropagates down thedendriteand triggers a series ofaction potentialswithin thesomaof the olfactory receptor cell. - Finally, the
action potentialspropagate continuously down the olfactory nerve axon.
Mixed Representation:
- Neuron responds to multiple features;
- Each neuron involves in multiple information representation;
- It implies population coding.
Temporal patterns:
- odors are inherently slow stimuli.
- Temporal coding, which depends on the timing of spikes, might instead encode the quality of odors (i.e., very subtle
difference between odors, can be obtained by training).
Neural Information Encoding
Neural Coding is a process that transforms the sensed information into spike signals.
- By designing biological models
- Directly deriving from mathematical models
e.gstatistics or
probability.
Rate Coding
Information is expressed by firing rates of neurons. Three different averaging procedures:
- an average over time
- an average over several repetitions of the experiment
- an average over a population of neurons