CO C2 Instructions
Introduction
- Instructions and Instruction set are Language of the computer
- The Design goals are:
- Maximize performance
- Minimize cost
- Reduce design time
Our chosen instruction set is RISC-V.
Instruction characteristics
-
Type of internal storage in processer,
e.g Regs- Stack
- Accumulator
- General purpose register
- Register-Memory
- Register-Register:
load/store
-
The number of the memory operand in the instruction
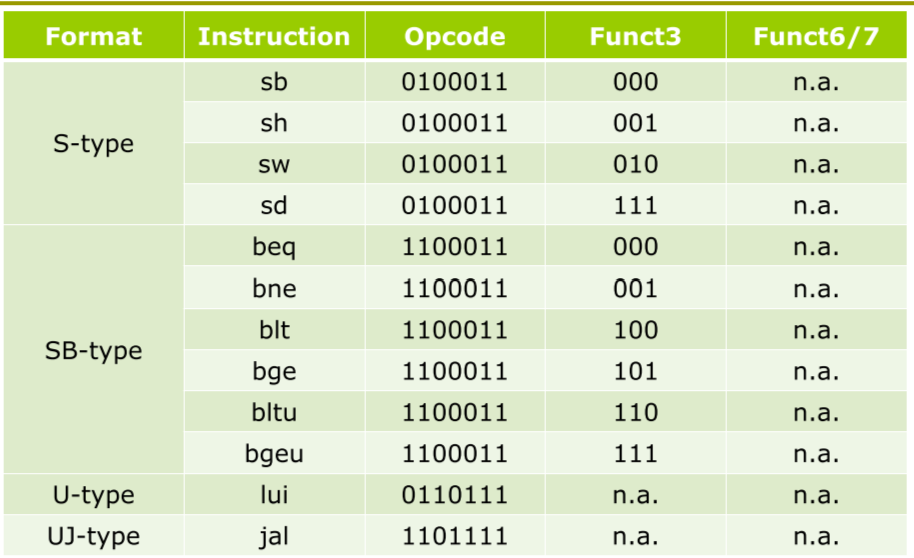
Instruction Type Maximum number of operands Number of memory addresses Register-Register 3 0 Register-memory 2 1 Memory-memory 2 / 3 2 / 3 -
Operations in the instruction Set
-
Type,
e.g Reg/Memoryand Size of Operandse.g 32/64 -
Representation in the Computer: Encoding
Variables difference
- in C :
int, char, float - in Instruction Set :
RegisterMemory addresswith Displacement ,ImmediateStack
Design Principle
- Simplicity favors regularity.
- Smaller is faster.
- Make the common case fast.
Operations and Operands of the Computer Hardware
Operation
Every computer must be able to perform arithmetic:
- Only one operation per instruction;
- Exactly three variables / operands.
1 | |
Operand
Register Operands
-
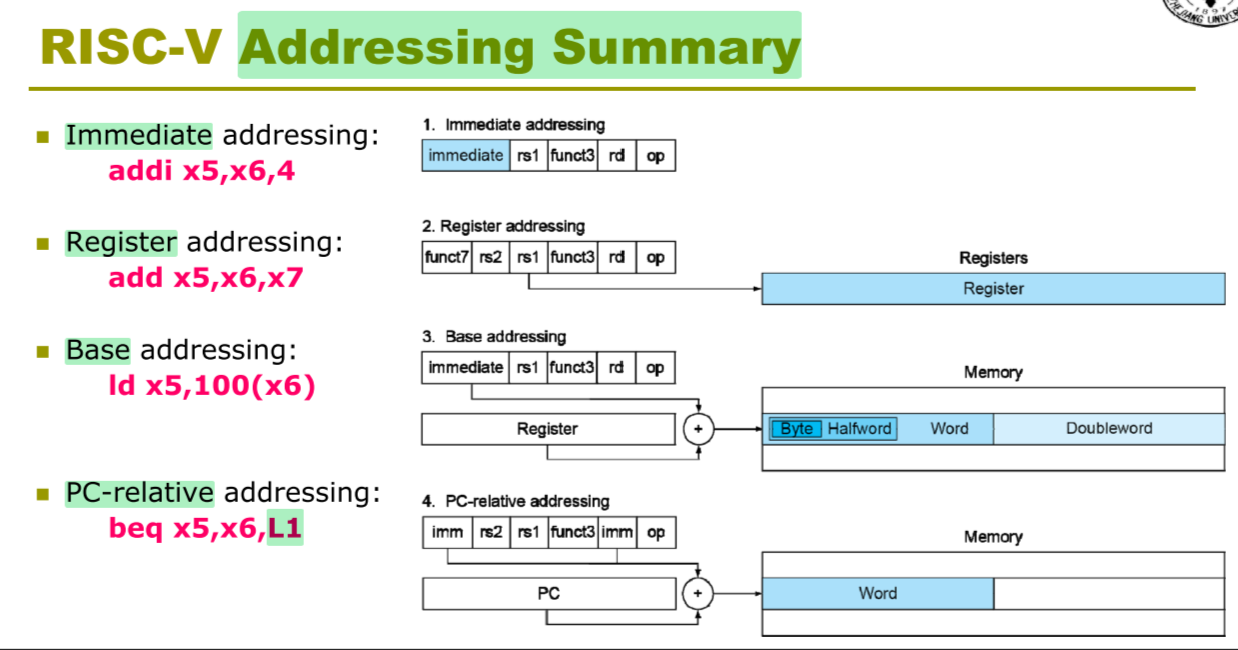
Arithmetic instructionsoperands must beregistersorimmediate. -
32 registers in RISC-V:
x0 - x31, 32 bits(word) /64 bits(doubleword) for each.Name Register Name Usage Preserved On call? x00 The constant value 0 n.a x1(ra)1 Return address(link register) y x2(sp)2 Stack pointer y x3(gp)3 Global pointer y x4(tp)4 Thread pointer y x5-x75-7 Temporaries n x8-x98-9 Saved y x10-x1710-17 Arguments/results n x18-x2718-27 Saved y x28-x3128-31 Temporaries n
寄存器个数的增加会导致指令中表示寄存器的bit增加。
Memory Operands
-
save much more data and complex data structures
-
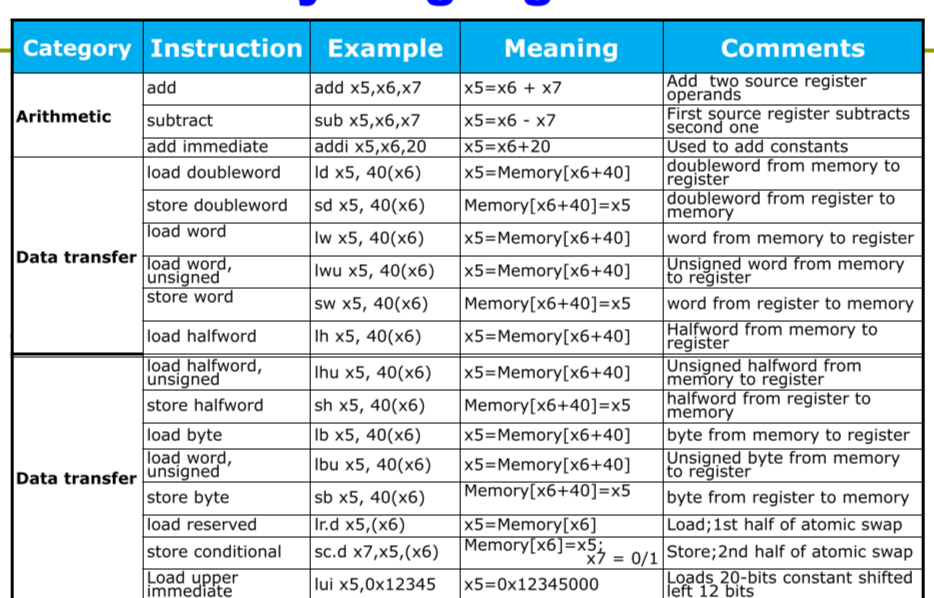
Data transfer instructions:
load,store1
2
3
4
5ld a,i(b) #from memory b[i] to register a, 64 bits
lw c,i(d) #32bits
sd a,i(b) #from register a into memory b[i]
sw c,i(d)
# i must be an immediate!
- In RISC-V: Memory Accessed only by data
transfer instructions. - Byte addressed: Each address identifies an 8-bit byte.
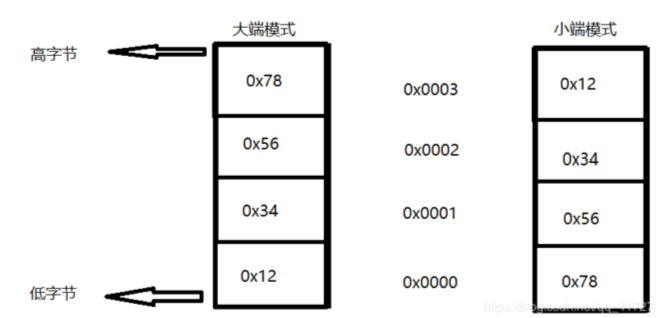
按照byte(8bits)寻址,即对于一个bits长的地址,可以寻址到个地址。 - Little Endian: Least-significant byte at least address of a word.
- Memory Alignment ? NOT REQUIRED!
Endianness/byte order
- Big endian:数据的高字节存放在低地址,低字节存放在高地址.
e.g PowerPC - Little endian: 数据的高字节存放在高地址,低字节存放在低地址.
e.g RISC-V
e.g32位机器上存放0x123456789:
处理时一般从低地址开始处理。大端方便人阅读;小端方便机器处理,也是机器架构的主流。
Registersare faster to access than memory.- Operating on
memory datarequiresloadsandstores - Compiler must use registers for variables as much as possible.
- Spilling registers: Putting less commonly used variables(or those needed later) into
memory - Register optimization
- Spilling registers: Putting less commonly used variables(or those needed later) into
Constant or Immediate Operand
1 | |
signed and unsigned numbers
Bits are just bits (no inherent meaning),but there are conventions define relationship between bits and numbers.
-
Unsigned:
-
2’s-Complement Signed:
-
Sign Extension: Replicate the sign bit to the left; extend with 0s for unsigned values.
1
2lb a,i(b)
lbu a,i(b)
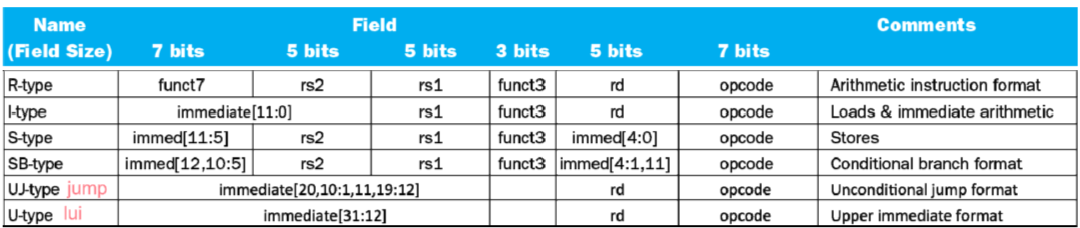
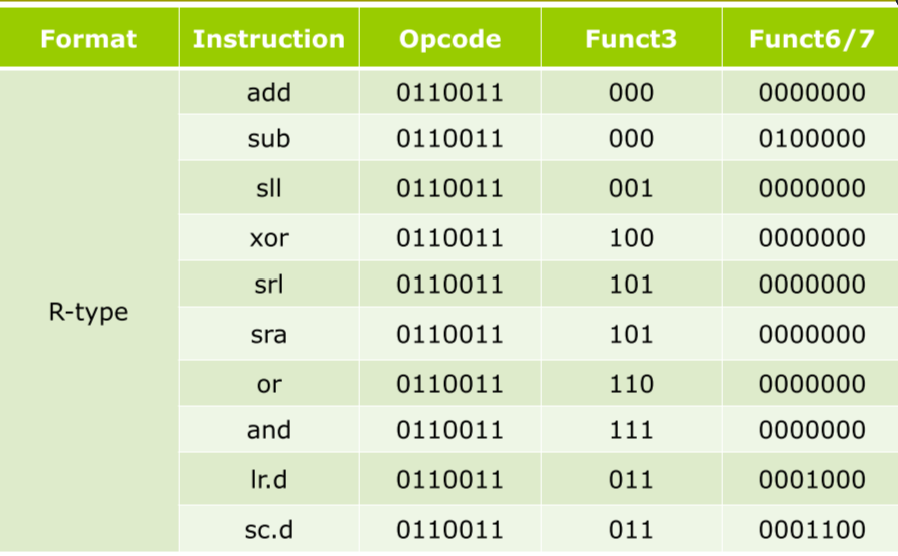
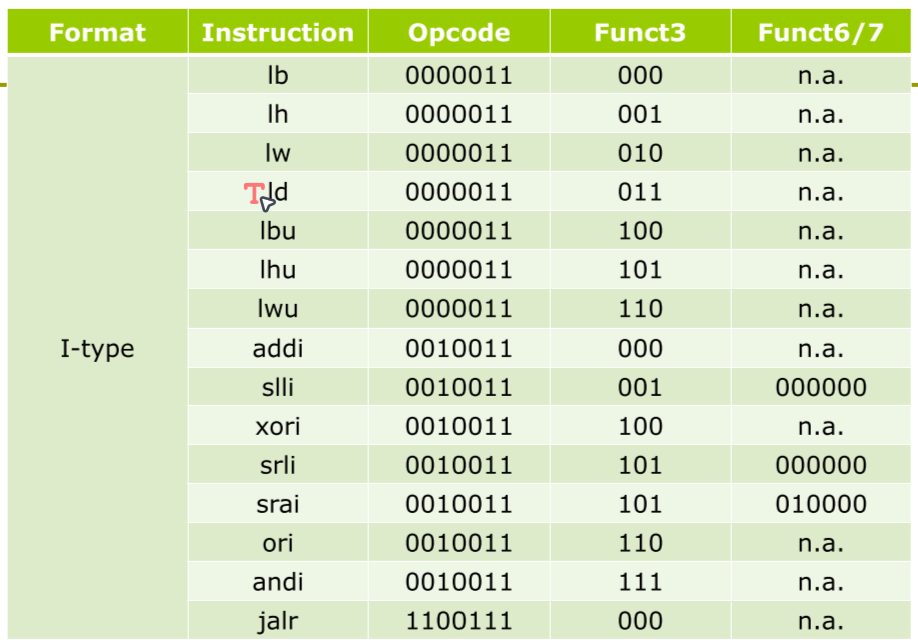
Representing Instructions in the Computer
Stored-program
Instructions are represented as numbers
Programs can be stored in memory like numbers
Instructions represented in binary, just like data
Instructions and data stored in memory
Programs can operate on programs
e.gcompilers, linkers, …Binary compatibility allows compiled programs to work on different computers, Standardized ISAs
Logical Operation
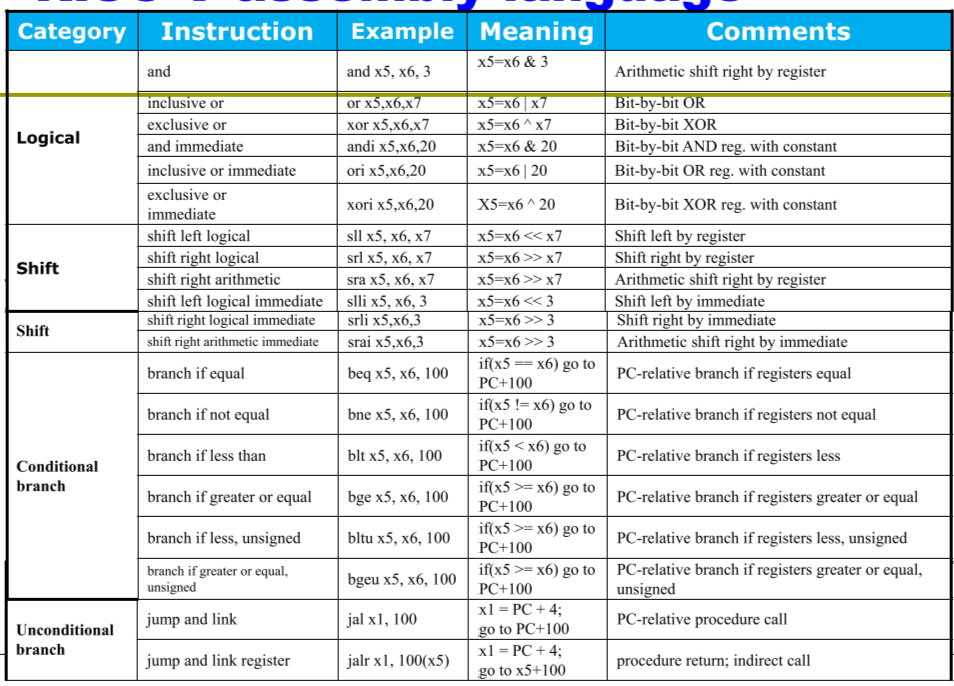
Instructions for Making Decisions
Supporting Procedures in Computer Hardware
Procedure/function is be used to structure programs.
- A stored subroutine that performs a specific task based on the parameters with which it is provided
- easier to understand, allow code to be reused
Steps
- Place Parameters in a place where the procedure can access them (in registers x10~x17)
- Transfer control to the procedure
- Acquire the storage resources needed for the procedure
- Perform the desired task
- Place the result value in a place where the calling program can access it
- Return control to the point of origin (address in x1)
Instructions
Procedure call: jump and link
1 | |
Procedure return: jump and link register
1 | |
Using More Registers
Stack:Ideal data structure for spilling registers. For saved registers, the callee saves in satck and restores them back.
- Stack pointer
sp - grow from higher address to lower address.
- Push: sp= sp-8
- Pop: sp = sp+8
1 | |

Communicating with People
MIPS Addressing for 32 Bit Immediates and Addresses
Translanting and starting a Program
A C Sort Example to Put It All together
Arrays Versus Pointers
Real Stuff: IA-32 Instructions
Fallacies and Pitfalls
Concluding Remarks
Historical Perspective and Further Reading