DB C9 Query Processing
-
CPU can’t manipulate the data in disk directly.
-
The growth rate of the disk data transfer(read/write) speed is much slower than that of the disk size.
In 20 years, disk size: 1000 times; read/write speed: 40 times
-
The growth rate of the disk seek speed is much slower than that of the disk data transfer speed.
Overview
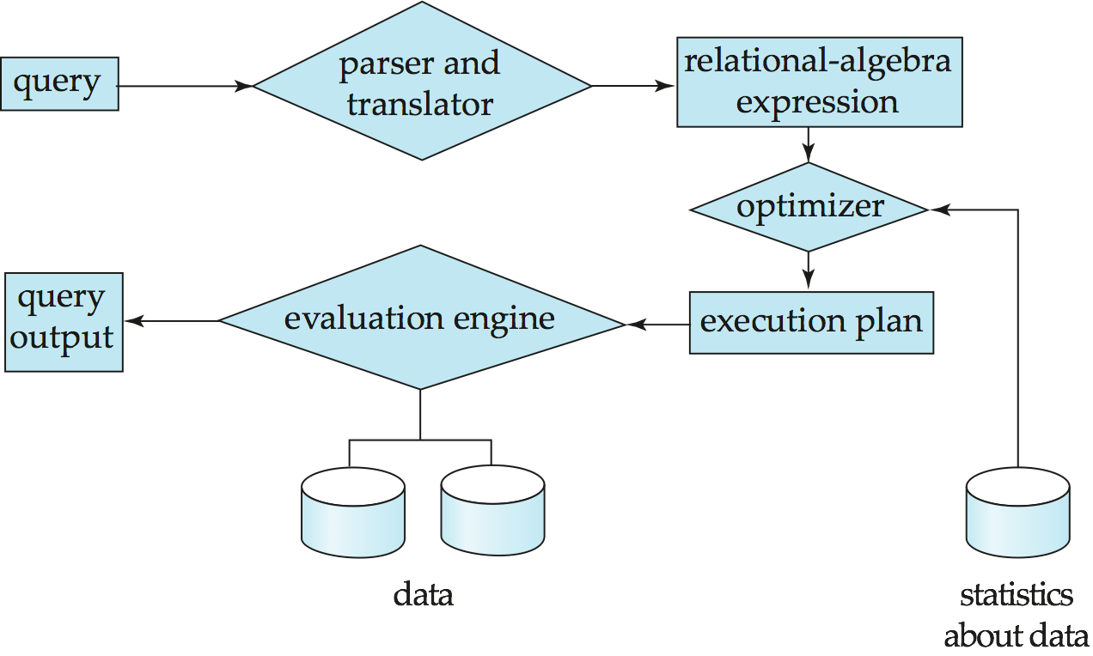
Basic Steps in Query Processing
-
Parsing and translation:
- Parser checks syntax, verifies relations.
- Translate the query into the internal form: extended relational algebra (ERA).
-
Optimization:
Why optimization?
- For a given SQL query, there may be many equivalent relational algebra expressions.
- Each relational algebra operation can be evaluated using one of several different algorithms.
e.glinear search or scan
- Find out various
equivalent relational algebraexpressions. - A sequence of primitive operations which specify detailed evaluation strategy is called a query-execution/evaluation plan.
- Query Optimization: Among all equivalent evaluation plans choose the one with the lowest cost. Two factors are considered for cost:
- Cost is dependent on the algorithms of the executions.
- Cost is also estimated using statistical information from the database catalog.
-
Evaluation:
-
The query-execution engine takes a query-evaluation plan, executes that plan, and returns the answers to the query.
evaluation plan: Annotated expression specifying detailed evaluation strategy.
defines exactly
- what algorithm is used for each operation;
- how the execution of the operations is coordinated.
-
Measures of Query Cost
Cost is generally measured as total elapsed time for answering query. Factors are:
-
Disk access
-
CPU
-
Network communication
-
……
Consider these factors under actual circumstances.
Disk access
Typically disk access is the predominant cost, and is relatively easy to estimate.
disk access is measured by taking into account:
-
Number of seek operations performed
-
Number of blocks read average-block-read-cost
-
Number of blocks written average-block-write-cost
:
Data is read back after being written to ensure that the write was successful
Simplified measure
We just use the ①number of block transfers from disk and ②the number of seeks as the cost measures.
- : time to transfer one block. (≈ 0.1ms)
- : time for one seek. (≈ 4ms)
Selection Operation
Basic algorithms
File scan
Search algorithms that locate and retrieve records satisfying a selection condition, do not use index.
Algorithm A1 (linear search).